MATCHA INSIGHT is a knowledge series for professionals, exploring matcha from grinding and quality to production and distribution — based on hands-on testing and real industry practice.
Matcha Production

Part 1 - Cultivating Matcha: The Shading Method
Among Japanese teas, tencha (the raw material for matcha), gyokuro, and kabusecha are grown using a special method called “shading cultivation” (hifuku saibai), in which the new shoots are not…
matchadirect.kyoto/blogs/matcha-insight
Part 2 - Harvesting Matcha: Selecting the Finest Leaves
Hand-picking and scissor harvesting The harvesting methods for tencha, the raw material of matcha, are broadly divided into two types: “hand-picking” and “scissor harvesting.” Hand-picking, as the term suggests, is…
matchadirect.kyoto/blogs/matcha-insight
Part 3 - Processing Matcha: From Fresh Leaves to Tencha
Tea farmers immediately transport the freshly plucked leaves to a crude tea factory, where they are processed into “crude tea.” Crude tea is made by steaming and then drying fresh…
matchadirect.kyoto/blogs/matcha-insight
Part 4 - Refining Matcha: The Finishing of Tencha
Finishing Process Matcha manufacturers take the crude tea produced through the tea farmer’s primary processing of fresh leaves and further process it into finished products. Taking into account flavor, production…
matchadirect.kyoto/blogs/matcha-insightMatcha Knowledge

Does Matcha Expire? Understanding Its Shelf Life and How to Keep It Fresh
We often receive questions from customers such as, "How long is the shelf life of matcha?" One distinguishing feature of matcha compared to other teas is its relatively short shelf…
matchadirect.kyoto/blogs/matcha-insight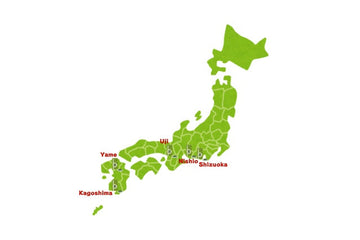
Where Is Matcha Grown? Japan’s Major Matcha Regions
Here is an introduction to Japan’s main matcha-producing regions: *Uji, Nishio, and Yame are regions known for tea production, while Kagoshima and Shizuoka are entire prefectures recognized as major tea-producing…
matchadirect.kyoto/blogs/matcha-insight
What is Gogumi? Understanding Matcha Blend
The Essence of Uji Matcha Production When it comes to matcha in Japan, Kyoto's "Uji Matcha" is the gold standard. Supporting its exceptional quality is the practice of gogumi (blend),…
matchadirect.kyoto/blogs/matcha-insight
Matcha Glossary

Matcha Cultivation & Harvesting Glossary
Shading Cultivation: A cultivation method in which tea plants are covered to reduce sunlight from the emergence of new shoots until harvest. Materials such as rice straw and synthetic shading…
matchadirect.kyoto/blogs/matcha-insight
Matcha Processing Glossary
Fresh Tea Leaves: Tea leaves immediately after plucking. Freshness control directly affects colour and flavour. Leaf Pit: A temporary holding unit used before the steaming step. Cold air is supplied…
matchadirect.kyoto/blogs/matcha-insight
Matcha Grinding Glossary
Grinding Methods: Matcha is generally ground using two main methods: stone milling and mechanical grinding. Stone milling produces a small output (around 40–50 g per hour) but is associated with…
matchadirect.kyoto/blogs/matcha-insight
Matcha Types & Grades Glossary
Usucha / Koicha: Originally, these terms describe two preparation styles of matcha: usucha (thin tea) and koicha (thick tea). In general, usucha is prepared by whisking about 2 g of…
matchadirect.kyoto/blogs/matcha-insight
Matcha Distribution & Logistics Glossary
Tea Grower: A producer who cultivates and harvests tea leaves and manufactures aracha (primary processed tea) for shipment. In Uji, many growers are not exclusively tea farmers and may also…
matchadirect.kyoto/blogs/matcha-insight
Matcha Preparation Glossary
Usucha (Thin tea): A basic preparation style in which matcha is whisked to create foam and enjoyed in a light, refreshing way—typically using 2 g of matcha with about 60…
matchadirect.kyoto/blogs/matcha-insight
